Transistors come in a lot of different types, but in this article, I’m only going to be talking about bipolar junction transistors (BJTs). Specifically, I’m going to be talking about NPN transistors and how they’re different from PNP transistors.
A transistor is a component that’s very commonly used in guitar pedals and other electronics. If you have no interest in how transistors are used in guitar pedals, I’m going to start with the main difference between NPN and PNP transistors, then go into how they’re used for guitar pedals; so there’s still plenty of information here for everybody!
In guitar pedals, transistors are usually used to amplify a sound signal. Depending on how the transistor is used in a pedal, it will either be in its active or saturation region; i.e. it will be used to just amplify, or used to amplify and distort. Outside of guitar pedals, transistors are used not only for signal amplification, but also as fast switches in computers and other electronics. From there, transistors are also the building blocks of a lot of integrated circuits.
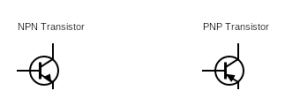
NPN Versus PNP Transistors
“NPN” stands for negative-positive-negative. On the flip side, PNP stands for “positive-negative-positive.”
All this means is that an NPN transistor consists of a positive semiconductor sitting between two negative semiconductors. PNP transistors, on the other hand, is a negative semiconductor sitting between two positive semiconductors. For both types of transistors, it’s the base that’s in the middle.
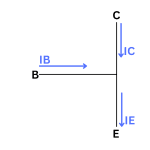
What this means for how these two types of transistors operate is that the current flows in opposite ways, with an NPN transistor having the current flow from collector to emitter and a PNP transistor having current run from the emitter to the collector. Because of this, the choice of whether to use a PNP or NPN transistor will depend on how the circuit is designed, where the current is flowing, and where you want it to flow.
Beyond this difference in polarity, NPN transistors tend to perform switching faster and handle higher currents better. PNP transistors on the other hand can handle higher voltages better.
For a lot of hobbyist applications of bipolar junction transistors, especially at the lower voltages home electronics builders use, the need for one type of a transistor needing to handle voltage or current isn’t really a concern, so the difference and choice of transistors really comes down to circuit design.
The Difference Between NPN And PNP Transistors In Guitar Pedals
In guitar pedals, NPN transistors tend to be far more common. Because the most common form of power wiring in guitar pedals is with a centre positive approach using negative ground, NPN is generally the best way to design a circuit. That being said, PNP transistors aren’t unheard of in guitar pedals.
Some older circuits that used a positive ground may use PNP transistors, or circuits like the Harmonic Jerculator uses both NPN and PNP.
Since the main difference between NPN and PNP transistors is just current flow, it’s also positive to convert a PNP circuit to an NPN circuit, and vice versa, and it should sound the same.
Do PNP And NPN Transistors Sound Different In Guitar Pedals?
I did some research on this, and while some people swear there’s a difference in sound between NPN and PNP transistors, I don’t buy it. In truth, the two types of transistors should sound identical. However, silicon and germanium transistors do sound very different. Since a lot of older pedal circuits used a positive ground, a lot of them used PNP transistors. These older circuits tended to use germanium transistors as well. As the power paradigm shifted negative ground, the use of silicon transistors also became a lot more common in guitar pedals. These transistors also tended to be NPN. Since germanium and silicon transistors sound different, it may be possible that that’s where this misunderstanding came from.
Other than that, a transistor’s beta value will effect how much gain it gives, which can also effect the sound and tone of the final signal. But, assuming an NPN and PNP transistor have the same beta/hFE, they should sound the same (barring any general differences int he transistor’s design).
All in all, the difference between NPN and PNP transistors just comes down to how the current flow. For some applications, you may want to rely on the strengths of one over the other, but that’s less of a concern for hobby or consumer electronics.
Related posts:
 Ultimate Guide To Transistors In Guitar Pedals: What They Do And How They Work
Ultimate Guide To Transistors In Guitar Pedals: What They Do And How They Work
 What Is Transistor hFE?
What Is Transistor hFE?
 The Difference Between Silicon And Germanium Transistors
The Difference Between Silicon And Germanium Transistors
 Ultimate Guide To Resistors In Guitar Pedals: What They Do And How They Work
Ultimate Guide To Resistors In Guitar Pedals: What They Do And How They Work
 Ultimate Guide To Diodes In Guitar Pedals: What They Do And How They Work
Ultimate Guide To Diodes In Guitar Pedals: What They Do And How They Work
 Transistor Saturation, Active, And Cutoff Region
Transistor Saturation, Active, And Cutoff Region
 What Is Gain (And How It’s Different From Volume)
What Is Gain (And How It’s Different From Volume)
 What Are Coupling Capacitors?
What Are Coupling Capacitors?
 How Does A Drive, Gain, Or Distortion Knob Work?
How Does A Drive, Gain, Or Distortion Knob Work?
 How To Wire Guitar Pedal Enclosures
How To Wire Guitar Pedal Enclosures
